Learn how to do Mutual TLS in Quarkus apps
In this entry, we explore how to set mutual TLS encryption between two Quarkus applications manually. Both on bare metal and Kubernetes.
What is Mutual TLS Authentication?
Mutual TLS authentication or two way authentication is an extension of Transport Layer Security (or “TLS”), and it ensures that traffic between the client and server is secure and trusted in both directions.
Why Mutual TLS?
It is an additional security layer which verifies not only the server identity but also the client one.
How implement it?
The best approach to implement Mutual TLS between two services is to delegate it to the infrastructure, for instance, a Service Mesh. This achieves a standard and secure way of communication and avoids that each application implements its solution. However, you are not always working on cutting edge environment.
Let’s have a look at how to implement mTLS with Quarkus if you don’t have a service mesh environment like Istio.
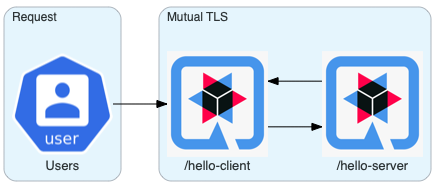
Bootstrapping
Let’s create both the server and client applications we will secure.
mvn io.quarkus:quarkus-maven-plugin:1.4.1.Final:create \
-DprojectGroupId=org.acme \
-DprojectArtifactId=quarkus-server-mtls \
-DclassName="org.acme.server.mtls.GreetingResource" \
-Dextensions="rest-client, resteasy-jsonb, kubernetes-client" \
-Dpath="/hello-server"mvn io.quarkus:quarkus-maven-plugin:1.4.1.Final:create \
-DprojectGroupId=org.acme \
-DprojectArtifactId=quarkus-client-mtls \
-DclassName="org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingResource" \
-Dextensions="rest-client, resteasy-jsonb, kubernetes-client" \
-Dpath="/hello-client"Certificate and Truststore generation
Of course, you need a server, client certificates and a truststore :)
keytool -genkeypair -storepass password -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -dname "CN=server" -alias server -ext "SAN:c=DNS:localhost,IP:127.0.0.1" -keystore quarkus-server-mtls/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/server.keystore
keytool -genkeypair -storepass password -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -dname "CN=client" -alias client -ext "SAN:c=DNS:localhost,IP:127.0.0.1" -keystore quarkus-client-mtls/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/client.keystoreFor this example, we are simulating a truststore using:
-
client.keystoreas truststore for the server application. -
server.keystoreas truststore for the client application.
cp quarkus-server-mtls/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/server.keystore quarkus-client-mtls/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/client.truststore
cp quarkus-client-mtls/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/client.keystore quarkus-server-mtls/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/server.truststoreHello Server Application
Let’s open and configure the server quarkus-server-mtls
Enable SSL on the Hello Server Application
Add the following properties to enable SSL in your application src/main/resources/application.properties
quarkus.ssl.native=true
quarkus.http.ssl-port=8443
quarkus.http.ssl.certificate.key-store-file=META-INF/resources/server.keystore
quarkus.http.ssl.certificate.key-store-password=password
quarkus.http.port=0
quarkus.http.test-port=0| See the guide Using SSL with Native to explore in details how SSL works in Quarkus. |
Activate client authentication
quarkus.http.ssl.client-auth=required
quarkus.http.ssl.certificate.trust-store-file=META-INF/resources/server.truststore
quarkus.http.ssl.certificate.trust-store-password=passwordUpdate GreetingResource
To better see that the response is coming from the server application, let’s update the org.acme.server.mtls.GreetingResource class.
@Path("/hello-server")
public class GreetingResource {
@GET
@Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)
public String hello() {
return "hello from server"; (1)
}
}| 1 | Change the return statement in "hello from server" |
And the test class.
@QuarkusTest
public class GreetingResourceTest {
@Test
public void testHelloEndpoint() {
given()
.when().get("/hello-server")
.then()
.statusCode(200)
.body(is("hello from server")); (1)
}
}| 1 | Change the matcher in "hello from server" |
Run it
mvn quarkus:devIf everything is correct when you try to hit the /hello-server endpoint, you should expect the following error.
curl -k https://localhost:8443/hello-server
curl: (35) error:1401E412:SSL routines:CONNECT_CR_FINISHED:sslv3 alert bad certificateThis means that your client (curl) did not provide a trusted certificate when it connected to the server.
Hello Client Application
At this point, the server application is ready to accomplish Mutual TLS. Let’s open and configure the client quarkus-client-mtls
Add Rest client for the server application
@Path("/")
@ApplicationScoped
@RegisterRestClient
public interface GreetingService {
@GET
@Path("/hello-server")
@Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)
String hello();
}Inject the GreetingService rest client on org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingResource.
@Path("/hello-client")
public class GreetingResource {
@Inject (1)
@RestClient (2)
GreetingService greetingService;
@GET
@Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)
public String hello() {
return greetingService.hello(); (3)
}
}| 1 | CDI @Inject annotation. |
| 2 | MicroProfile @RestClient annotation. |
| 3 | Replace the return statement with the greetingService.hello();. |
| See the guide rest-client to explore in details. |
Update the unit test
Add quarkus-junit5-mockito dependency to your project.
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-junit5-mockito</artifactId>
</dependency>@QuarkusTest
public class GreetingResourceTest {
@InjectMock (1)
@RestClient (2)
GreetingService greetingService;
@Test
public void testHelloEndpoint() {
Mockito.when(greetingService.hello()).thenReturn("hello from server"); (3)
given()
.when().get("/hello-client")
.then()
.statusCode(200)
.body(is("hello from server"));
}
}| 1 | Inject the CDI bean. |
| 2 | RestClient type. |
| 3 | Mock the hello request. |
| See the guide Testing to explore in details. |
Configure MicroProfile rest client for Mutual TLS
Add the following properties to enable SSL in your application src/main/resources/application.properties
org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingService/mp-rest/url=https://localhost:8443
org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingService/mp-rest/trustStore=classpath:/META-INF/resources/client.truststore
org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingService/mp-rest/trustStorePassword=password
org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingService/mp-rest/keyStore=classpath:/META-INF/resources/client.keystore
org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingService/mp-rest/keyStorePassword=password
quarkus.ssl.native=trueExternal Configuration
You do not want to have a certificate inside your application and Quarkus allows you to use external configuration and override the runtime application properties.
Let’s check how we can do in Kubernetes / OpenShift.
During the application boostrapping you added the kubernetes-config extensions. The extension works by reading ConfigMaps directly from the Kubernetes API.
|
In case you are in a restricted environment which not allow the role to view ConfigMap to your service account, you need to mount the external The working directory for:
volumeMounts sample
# ...
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
name: client
# ...
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /deployments
|
Secret
Create server, client and truststore secret which contains your certificates and truststore. For instance:
kubectl create secret generic server --from-file=tls/server/
kubectl create secret generic client --from-file=tls/client/
kubectl create secret generic truststore --from-file=tls/ca/truststoreConfigMap
Create the server and client ConfigMap.
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: server
data:
application.properties: |
quarkus.http.ssl.certificate.key-store-file=/deployments/tls/server.keystore
quarkus.http.ssl.certificate.key-store-password=password
quarkus.http.ssl.certificate.trust-store-file=/deployments/tls/ca/truststore
quarkus.http.ssl.certificate.trust-store-password=passwordkind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: client
data:
application.properties: |
org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingService/mp-rest/url=https://server:8443
org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingService/mp-rest/trustStore=/deployments/tls/ca/truststore
org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingService/mp-rest/trustStorePassword=password
org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingService/mp-rest/keyStore=/deployments/tls/client.keystore
org.acme.client.mtls.GreetingService/mp-rest/keyStorePassword=passwordEnable kubernetes-config extension on the server and client application
Add the following properties for the server application:
# only when running in prod (Kubernetes environment)
%prod.quarkus.kubernetes-config.enabled=true
quarkus.kubernetes-config.config-maps=serverand the client application:
# only when running in prod (Kubernetes environment)
%prod.quarkus.kubernetes-config.enabled=true
quarkus.kubernetes-config.config-maps=client| See the guide Kubernetes Config to explore in details. |
Deploy Everything
Here an example for the client application:
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: client
namespace: mtls
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: client
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: client
spec:
volumes:
- name: client
secret:
secretName: client
- name: truststore
secret:
secretName: truststore
containers:
- name: client
image: 'image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000/mtls/client:latest'
ports:
- containerPort: 8443
protocol: TCP
resources: {}
volumeMounts:
- name: client
readOnly: true
mountPath: /deployments/tls
- name: truststore
readOnly: true
mountPath: /deployments/tls/ca| See this instruction https://github.com/openlab-red/quarkus-mtls-quickstart/tree/master/deploy to explore in details. |
Conclusion
You have successfully implemented a Mutual TLS with Quarkus. The full Quarkus Mutual TLS example is available in the github repository mentioned in the links section.
Links
-
GitHub repository: https://github.com/openlab-red/quarkus-mtls-quickstart
